We read something to obtain some information. Every reading text, e.g. a textbook passage, a magazine article, a newspaper ad, a road sign, a letter, etc., has a message for the reader. And the reader’s aim is to get the right message as quickly as possible.
Introduction to Developing Reading Skills
To realise this goal, you as a reader should note the following things:
- You should have a reason for reading. Ask yourself, “Why am I going to read it?” before you start reading anything. You have gone to a restaurant, for example, for dinner. So you need to read the menu for ordering your meal. You are reading this book, because you may need to understand agricultural matters in English from a textbook, a booklet, a brochure, etc. So you need to understand English words and expressions used for describing some topics/subjects of agriculture. You may also need this proficiency if you teach agriculture in a school.
- Do not stop and look at every word when you read read several words at a time. In other words, read in chunks. If you look at and read every word you will be a very slow reader; and in paying attention to each word you are likely to miss out the most important point in reading, i.e. the message, the information contained in groups of words used in context, not in words used in isolation. Therefore, consider reading passages as a whole, rather than as a series of items. and structures.
- When you are reading for information, you should read silently. Reading aloud does not help students to develop their reading skills, though it can help them to practise pronunciation.
Twenty lessons under the first four units are written for developing the reading skills at various levels of difficulty. For example, the beginning lessons are built on reading instructions which are followed by lessons on more difficult reading tasks based on descriptions, reports and charts, process and technology.
Unit: 1 Developing the reading skills 1

Lesson 1.1 – Reading instructions 1
Objectives:
After you have studied the lesson you will be able:
– to follow written instructions or directions about how to grow vegetables,
– to use such words as loamy, friable, nursery beds, disinfect, sow, seedlings, transplant.
A. Look at the picture and try to say what the man is doing.

Fig : Nursery beds
A1. Read the text:
Jamil Ahmed is a successful farmer. He lives in a village in Sribordi thana. Yesterday he went to the Thana Agricultural Officer (TAO) and got a small book on how to grow vegetables. Today Jamil is reading the booklet to some of his neighbours. This is what the booklet says:
If you want to grow good vegetables you have to follow these instructions:
- Select a loamy, friable soil.
- Plough and break the soil properly.
- Mix manures into the soil.
- Disinfect the soil with boiling water.
- Mix the seeds with a little disinfected sand.
- Sow the seeds in the beds.
- Water the beds twice a day.
- Lift the seedlings from the nursery beds about 3 weeks after sowing.
- Now transplant the seedlings as soon as possible.
B. Study these words:
loamy (adj) – Loamy soil or loam does not contain too much sand or too much clay. This type of soil is good for growing vegetables and crops.
friable (adj) – easily broken up
friable soil – soil that you can break and prepare easily
nursery beds – seed-beds where seedlings are grown

disinfect (v) – destroy germs of diseases with disinfectants, i.e. germ- killing substances (germicides) in liquid or powder form
You can disinfect a wound or a place with dettol or other germicides. You can disinfect the soil of nursery beds with just boiling water.
sow (pt sowed, pp sown or sowed) – put or scatter seeds in or on the ground We can sow grass, jute, etc. We can sow a field with rice, wheat, etc.
seedlings (n, sing – seedling) – A seedling is a young plant newly grown from a seed.
transplant – remove a young plant with its roots and replant it elsewhere. We usually transplant aman paddy.
C. Match the expressions in Column A with the expressions in Column B. No. 1 is done for you.
No 1(f): For growing vegetables you should select an easily breakable soil.
D. Write directions/ instructions for someone who wants to grow tomatoes.
Use the following action verbs and clues. Use other necessary words to write the instructions.
Verbs : select, make, apply, use, sow, pour
Clues : a loamy soil, manures, seed-beds, germicides, seeds in rows, water, a plough or a spade
Example: Select a loamy soil for growing vegetables.

Lesson 1.2 – Reading instructions 2
Read the following instructions for making compost.
Plants need food for their healthy growth. Compost is perhaps the best food for plants. It is a good manure. It is made of such materials as leafy plants, rubbish, cowdung, poultry droppings, etc.
Here are some instructions or directions about how to make compost :
1) Collect enough plant materials like grasses, leaves, hyacinth, straw, shrubs, etc. waste materials like sweepings, dirty water, kitchen rubbish, rice hulls, etc. and farmyard manures like cowdung, poultry droppings, etc.
2) Make a bamboo or wooden container inside or near your garden.
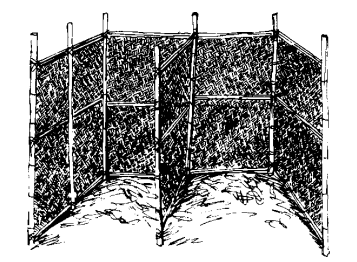
Fig : A container
3) Make the container 2.4 metres long, 1.2 metres wide and 1.2 metres high. Put a removable partition with bamboo or wood in the middle so that you have two bins.
4) Deposit in one of the bins about a 30-cm layer of plant and waste materials.
5) Put about an 8-cm layer of farmyard manures such as cowdung or poultry droppings on top of the layer.
6) On top of it put a thin layer of soil.
7) Sprinkle some water on the soil. Make the materials moist, but not wet.
8) Repeat the whole process twice more until your pile rises to the upper limit of the bin, ie until it becomes 1.2 m high.
9) Cover the top of the pile with bamboo mats or a straw roof to protect it from the sun and rain.
10) Remove the partition after 2 weeks and put the rotten materials into the other bin.
11) Make more compost in the emptied bin, following the same process.
The removed pile of rotten materials becomes good compost after another 2/3 weeks. Now it is ready for use.

Study these words.
compost (n) – a kind of fertilizer made of rotten plants such as grasses, leaves, etc. and farmyard manures like
cowdung, poultry droppings, etc.
container (v contain) – anything such as a box, a bottle, etc used for holding something See the picture above.
bin (n) – A bin is also a container.
removable (adj) – which is not fixed. It can be removed or pushed aside and brought back to its former position.
poultry droppings – waste matter from the bowels of farmyard birds such as hens, ducks, etc.
Study the example :
(a) Collect enough plant materials (instruction).
(b) Enough plant materials can be/are collected (description).
While (a) is an instruction or direction, (b) is a description or statement, but both (a) and (b) tell about the same thing.
Now use should be, can be, could be, is/are and describe each of these directions for transplanting tomatoes:
1. Prepare the soil of the tomato beds several weeks before transplanting.
2. Put manures into the soil.
3. Put stakes in the beds.
4. Transplant the seedlings in rows 50 cms apart with 40 cms between seedlings.
5. Transplant tomato seedlings 5 to 6 weeks after sowing.

6. Cover roots well with earth.
7. Water the soil twice a day.
Example: 1) The soil of the tomato beds should be prepared several weeks before transplanting.

Lesson 1.3 – Reading instructions 3

Read the passage to answer the following question.
Bangladesh is a tropical country. Its climatic factors like temperature, rainfall, air, light, etc are favourable for the production of various crops. It is also a deltaic country. As a result, its topography and soil conditions are favourable for the growth of certain crops. Think about the vast expanse of flat land we have! Also the few hills we have are not very big and high.
Bangladesh is crisscrossed by hundreds of rivers big and small. They give the land a lot of alluvia after each flooding. This alluvial soil is fertile and easy to prepare for cultivation.
Question:
Explain how the vast expanse of our flat land and hundreds of our rivers are favourable for growing various crops.
Read the following text to answer the question that follows.
A wide variety of tropical crops is grown in Bangladesh throughout the year in three distinct cropping seasons. These are:
(i) The spring or pre-monsoon season (March-May)
This season with moderate temperature and humidity, and occasional rainfall produces a lot of rice (aus), jute, sugarcane, vegetables, etc.
(ii) The monsoon season (May-September)
This season with high temperature and humidity, low solar energy and heavy rainfall is suitable for the growth of rice (T aman”), oil seeds, vegetables, etc.
(iii) The rabi season (October-March)
With low humidity and temperature this dry season produces a variety of crops, such as boro rice, wheat, potatoes, pulses, spices, mustard, vegetables, etc.

Question:
Suppose you are a Department of Agricultural Extension Specialist. You are writing a booklet to inform farmers about which crops they should grow in what seasons. Explain why they should do so. Find a calendar that shows both English and Bengali months and write the pieces of information either in the form of instruction/direction or in the form of description or in both.
Study these words.
a tropical country – a country situated between about 23.5″ north and 23.5° south of the equator. See a world map for a clear idea.
Bangladesh is situated between about 20 and 27° north of the equator. So according to its geographical position, Bangladesh is a tropical country. A tropical country is hot and humid. It has rainy and dry seasons.
favourable (adj) – helpful a deltaic country a country having flat alluvial area with some big rivers
topography (n) – geographical features like rivers, valleys, hills, mountains, roads, etc of a place
expanse (n) – wide and open area move crosswise; one cutting across another. Many rivers crisscross the whole of Bangladesh.
crisscross (v) – alluvia (n, sing alluvium) – soil consisting of mud, silt and sand deposited by flowing water, especially by flood-water
distinct (adj) – clear; separate
moderate (adj) – not extreme; having neither too much nor too little of something
temperature (n) – degree of heat and cold; high temperature, low temperature, etc.
humidity (n) – moisture in the air; dampness in the air

monsoon (n) – a season in Southern Asia (including Bangladesh, India and other countries around the Indian Ocean) with heavy rain. and high temperature

Lesson 1.4 – Reading events
Look at the pictures. They are not numbered (1,2,….. 8) in the right order. Try to think about the story of the woman in the picture and write the numbers of the pictures sequentially, i.e. in the order the events in her life happened. Now read the story and check your answer.
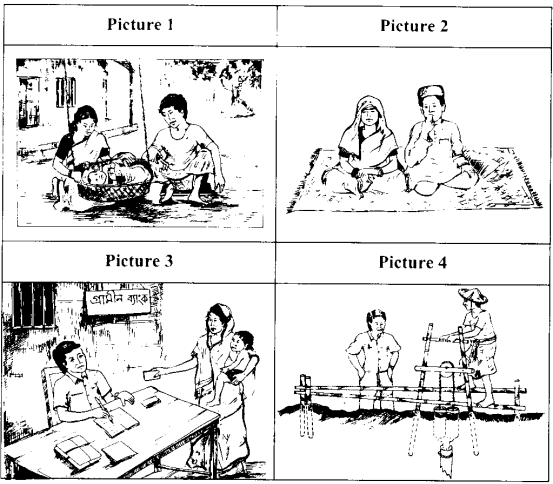
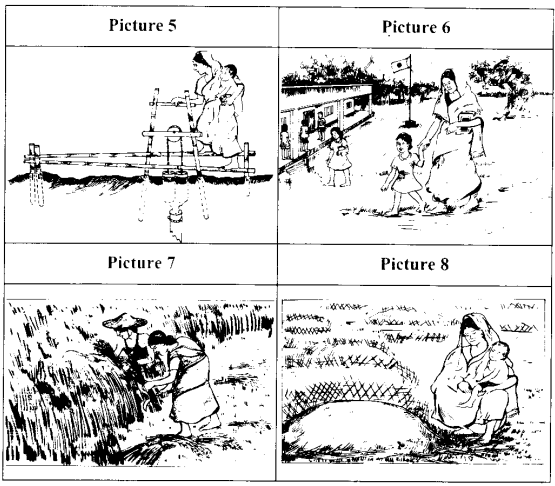
Fig : Events in a woman’s life
Majeda Begum was a village girl. She was the oldest among her 3 sisters and 2 brothers. Majeda went to school. But when she was in class 5, her father died and she had to leave school. Majeda was a hard-working girl. She used to work in some farmers’ houses in the village. With the little money she earned, the little amount of rice she got from the farmers’ wives. Majeda helped her family to survive.
Majeda was married when she was only 17 to Halim, 20, in the same village. They were a happy couple. Together they worked hard and in 4 years they could buy a plot of land. In the 5th year of their marriage they had a lovely daughter, Ayesha.
But their happiness did not last long. To celebrate their 7th marriage day Majeda was cooking some special food in the afternoon. Suddenly she was called outside. Some villagers brought Halim’s dead body in the yard. He was probably bitten by a snake while he was cutting jute in his field.
At first Majeda could not think about anything. But one thing she thought she must do. And that was to raise little Ayesha properly. So she took a loan from the Grameen Bank, bought a treadle pump and had it installed in her field. The Thana Agricultural Extension Officer helped her a lot.
Majeda is now happy. She herself operates the pump and irrigates the field when necessary. Now she grows enough rice for her and Ayesha. If you ask her, “What is the happiest day in your life?” she will answer, “I have three happiest days not one in my life. They are: the day I was married, the day Ayesha was born and the day the treadle pump came to my field.”

Study these words.
survive (v) – to cope with difficult circumstances; to continue to live or exist in adverse or difficult situations or conditions
celebrate (v) – to enjoy oneself on a special occasion; to celebrate, for example a birthday, a marriage day, a team’s victory in the football match, etc.
bitten (pp. pr t bite. pt bit) – A dog can bite a man. but a man cannot or should not bite a dog.
raise (v, pt & pp raised) – to bring up; to look after install (v. n installation) to set up an apparatus or a piece of
equipment so that it is ready for use to install an air-conditioner, an intercom, etc.
irrigate (v, n irrigation) – to supply water to especially dry land
Here are the main events in the life of Mr Kamal Ahmed. Arrange the events in the order they happened and write a paragraph using them.
1. 1st job Agricultural Extension Worker, Sherpur district, 1983
2. Born 1960
3. Primary education, Kakilakura Primary School, Sribordi thana
4. Master’s in Tropical Crops, Houston University, Texas, 1988
5. Married 1984
6. SSC, 1st division, Bakshigonj High School, Jamalpur, 1975
7. 8. B Ag, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, 1982 HSC, 1st division, AM college, Jamalpur, 1977
Activity Write a paragraph about yourself (about 300 words) describing the main events in your life, such as date of birth, education, job, (if any).
Self-assessment
Choose the best answer.
1. How old was Majeda when Ayesha was born?
a. 17 years
b. 19 years
C. 22 years
d. 26 years
2. How old was Ayesha when her father died?
a.1 year
b. 2 years
C.3 years
d. 4 years
3. He was probably bitten by a snake. Which of the following can replace the underlined word in the sentence?
a. surely
b. nearly
c. likely to be
d. certainly
4.Majeda was determined to raise Ayesha properly.
This means that Majeda was going to
a. look after her (Ayesha’s) growth and education.
b. take her always into her lap.
C. give her to an orphanage for food and education.
d. teach her how to work together
5.What do you consider is the main strength of Majeda’s character?
a. strong determination
b. fear for Ayesha
C. concept of love
d. school education
